The renewable energy landscape in Europe faced several notable challenges in 2024, highlighting the complexities of transitioning to a cleaner energy future. Here are some of the key hurdles that energy producers, investors and purchasers had to face:
Underinvestment in energy storage and grid infrastructure
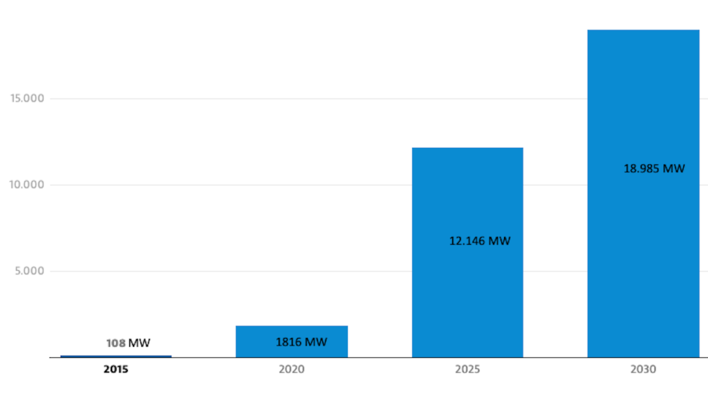
While renewable electricity generation has surged, investment in the supporting infrastructure has lagged behind: Energy Storage: Europe currently has around 8 GW of installed battery storage capacity, while the International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that 200 GW will be needed by 2030 to support the grid.
Also see: Expert analysis – How to approach battery energy storage systems in Europe
Grid modernisation: More than 150 critical grid reinforcement projects, requiring €180 billion in investment, have been identified to handle the demands of a renewables-heavy energy system. Without these investments, the clean energy transition risks bottlenecks in system reliability.
Resource shortage: In many countries, the large upgrade requirements cause a shortage of engineering and skilled labour resource, which means that even where the investments are being made, significant bottlenecks in the execution and delivery of the modernisation programmes might cause multi-year delays. This also applies to some extent to component supply.
Geopolitical and global market dynamics
Energy security risks: Continued geopolitical tensions, including conflicts in the Middle East and Russia-Ukraine, underscore vulnerabilities in energy security.
Government support and limited project availability: Generous government incentives in markets such as the UK, Italy, and France have made renewable projects increasingly competitive. In the UK we saw record-breaking auctions for Contract-for-Difference (CfD) support awarded 9.6 GW, but this has strained the pipeline for private buyers, potentially increasing PPA prices. In Italy oversubscription in agrivoltaics auctions (700 MW over capacity) signals strong demand but also heightened competition for project access.
As a result, buyers and developers are navigating a landscape of reduced project availability, rising PPA prices, and fierce competition against public auctions.
Looking ahead: opportunities and growth potential for 2025
Addressing these challenges requires greater investment in energy storage and grid infrastructure, along with proactive strategies to mitigate pricing and geopolitical risks. But there are also already growth opportunities visible both from a structural and a geographical perspective. These include:
Corporate Power Purchase Agreements (PPA)
We see a consolidation in Corporate PPA (Physical and Virtual) as most of them are increasingly prioritising renewable energy sourcing to meet sustainability goals. Also, Hybrid PPAs (solar + BESS or solar + wind) have emerged this year and it is expected to further increase in 2025, offering enhanced grid reliability and optimised revenue streams, reducing shaping cost. Across key markets in Europe, a significant pipeline of hybrid assets is ready to take if contractual arrangements can make the financial model bankable.
Also see: Expert analysis - The three strongest solar energy trends in 2025
Corporate buyers, particularly in the tech and manufacturing sectors, are showing the greatest interest in renewable energy. These industries are driven by decarbonisation commitments and cost predictability through long-term PPAs. Additionally, utilities and grid operators are investing in energy storage to enhance grid stability and integrate intermittent renewable sources effectively.
Multi-buyer, cross border and hydrogen PPA
Multi-buyer PPAs will also grow in 2025 as sellers are trying to standardise and simplify the contract structure. This structure entails an efficient way to mitigate the purchasers’ credit risk in a PPA. Typically, there is has the financial strength and credit rating to balance out non-investment grade corporates.
Cross-border PPAs are also expected to grow in the next year. This structure is mainly driven by Guarantees of Origin considerations and the search for a competitive PPA price.
Co-location projects
Co-location projects e.g. combining solar plants and storage becoming crucial as they enable better utilisation of grid connections, reduced costs, and optimised energy dispatch. Solar plants with integrated storage can mitigate intermittency issues, participate in ancillary services, and maximise revenue through peak shaving and arbitrage opportunities. Econergy’s response to these developments is a drive to expand our co-location developments, aiming to add BESS to existing solar developments where possible.
Geographical growth markets in Europe
As Econergy experiences continued growth in demand across Europe, we anticipate robust expansion in Italy, Romania, and Poland in 2025.
In Italy the updated PNIEC targets and the FER-X mechanism provide solid incentives for renewable energy projects. However, competitive and accessible frameworks for energy storage are critical to enhancing grid reliability and supporting Italy's ambitious energy transition goals.
Also see: SolarPower Europe report - EU solar market with only weak growth
Romania has a significant pipeline of solar and storage projects, positioning it as a key growth region, bolstered by favorable policy measures and market demand. In Poland the ongoing transition from coal is driving the need for clean energy solutions, with opportunities for both solar and storage projects to gain momentum.
The UK will remain a key market for storage and PPAs due to a mature PPA ecosystem and robust opportunities in the energy storage market.
Specific trends and hurdles in project financing and asset management
A shift towards long-term, flexible financing mechanisms is becoming increasingly prominent, with asset management adopting digitalisation and AI-driven tools for performance monitoring and predictive maintenance. These advancements are improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Also see: Romania – Econenergy secures financing for large-scale solar projects
Project financing trends differ by market, country, and revenue type (e.g., PPA, CfD). A significant trend is the reduced availability of funding for merchant solar PV projects in Europe, often coupled with lower leverage due to declining electricity price forecasts. However, this challenge is partially offset by the current reduction of key interest rates, which eases financial pressures.
Additional information about Econergy can be found here
Key hurdles include regulatory uncertainty, lengthy permitting processes, and grid connection bottlenecks. For technology providers, scaling production to meet rising demand and innovating cost-effective solutions are ongoing challenges. Addressing these hurdles requires:
- Policymakers to streamline permitting processes and establish clear, stable regulations.
- Grid operators to invest in infrastructure upgrades and enhance grid connection processes.
- Technology providers to focus on scalable, efficient solutions and collaborate with planners to tailor innovations to market needs.
These trends highlight the need for adaptable financing strategies tailored to specific market conditions. Technology integration and sustainable practices must be emphasised to drive project success and maintain construction surge. (Wolf Dietrich/hcn)