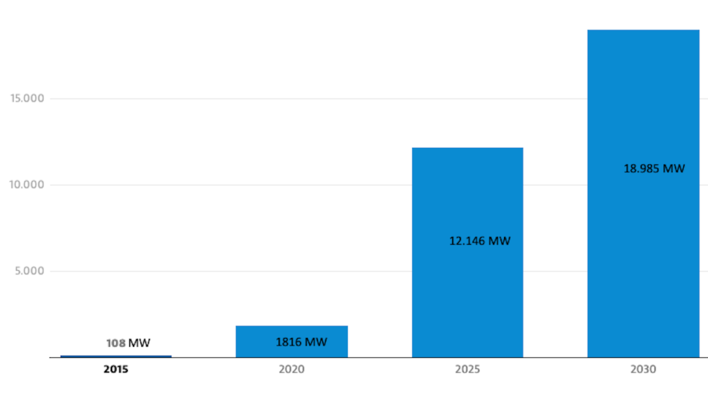
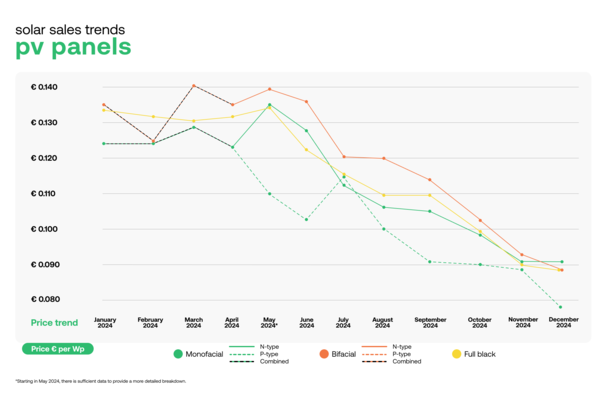
The winners of this year's awards were announced at The smarter E Europe industry trade fair. There are two categories for The smarter E Award.
Here are the winners in the Outstanding Projects category:
Centre for Renewable Energy Services (Bangladesh): The Sirris intelligent irrigation system supplies sensor-controlled pumps in Bangladesh with solar power and regulates automatic water distribution in the fields. On the one hand, this saves diesel, and on the other hand, irrigation only takes place until the necessary moisture is reached. Water consumption is reduced by at least 50 per cent. In addition to remote monitoring and control, the billing system is particularly noteworthy. This allows operator models that ensure long-term economic operation. Sirris thus has economic, ecological and sociological advantages. The optimised irrigation takes into account the different plant species as well as the pH value of the soil. The timing of the solar yield matches the irrigation needs.
Fenecon (Germany): The stationary storage system in Werdohl in Germany, consists of both car batteries that are still unused (zero use) and batteries that were already in use in Renault Zoe (second use). The storage system is installed in containers and is used as a storage unit for primary control power in the sense of grid stabilisation. In the future, energy management services will be offered to industrial customers and energy suppliers. In a container unit, 72 Zoe batteries with 40 kilowatt hours each are connected together to form a storage unit with a capacity of 2.88 megawatt hours. The batteries are operated in a stable and gentle manner.
Fluence Energy (Germany): The pilot project in Vilnius, Lithuania, is one of the first in the world to use a battery-based energy storage system in the transmission grid. This grid booster shows an extremely fast response with a processing time of 87 milliseconds and a complete switch from charging to generation in 70 milliseconds. It has been in trial operation since the end of 2021. Such grid boosters allow better utilisation of existing lines through time-delayed power transmission. They also reduce grid expansion when used at strategic grid nodes. For Lithuania, such a grid upgrade means more energy independence as well as higher decarbonisation through increased integration of renewable energy into the electricity grid.
Here are the winners of the Smart Renewable Energy category:
Fluence Energy (USA): with the Fluence IQ software platform, operators of renewable energy plants and energy storage systems generate automated bids for electricity supply and grid services. The software uses artificial intelligence to determine the optimal price based on various forecast parameters such as weather, demand and supply over a 24-hour time horizon, at which the plant operator can post its services on bidding platforms. With the software, operators optimise the financial return of an entire portfolio of generation plants as well as storage units, and reduce the amount of manual intervention at the control centre to achieve the optimised plant schedule.
Fronius International (Austria): The Fronius Wattpilot is an AC charging solution for charging from your own power generation at flexible electricity prices. With its automatic 1/3 phase switching, the Wattpilot offers a technical finesse for optimised charging of an electric vehicle across the entire power band from 1.38 to 22 kilowatts. Fluctuating surpluses from own generation can be optimally utilised. Vehicles that have lapsed into charging sleep are automatically woken up. In addition to the use of self-generated energy, the integrated connection to an electricity provider with flexible electricity prices (currently available in Germany and Austria) enables cost-optimised charging in more cost-effective price phases.
See also: BYD expects to deliver 250,000 Battery-Box systems in 2022
Transnet BW (Germany): The DA/RE (data exchange/redispatch) initiative is available to grid operators throughout Germany for active feed-in management. A digital platform is used to coordinate measures for grid stabilisation and congestion elimination through decentralised flexibility across all grid levels. With the help of the DA/RE platform, all players can fulfil a significant part of the new requirements of Redispatch 2.0 by streamlining the necessary coordination. Based on the automated congestion forecast, the coordination between the stakeholders becomes more efficient and ultimately serves a more secure and cost-effective management of the electricity grids. DA/RE reports to each grid operator at regular intervals the schedules and redispatch potentials of the respective Nabeg (Grid Expansion Acceleration Act) plants in their own grid. (HS/mfo)